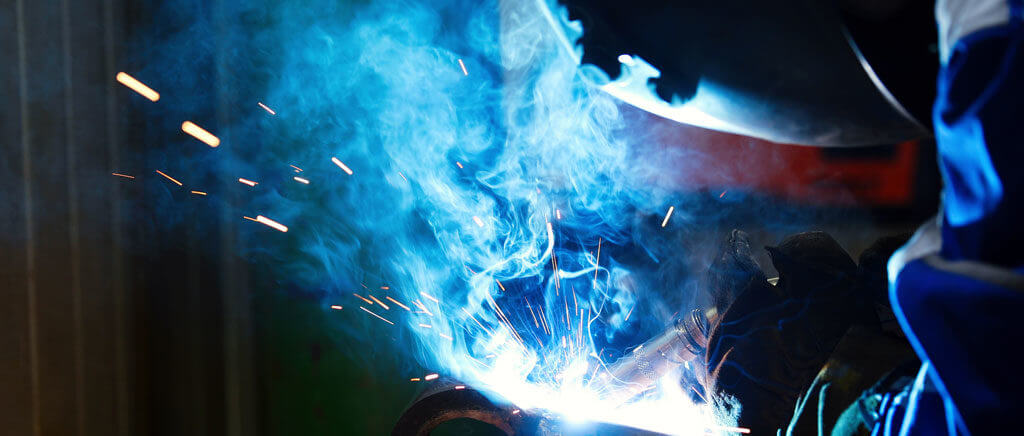
In 2008, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) introduced its National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP Rule 6X) as part of the Clean Air Act. The EPA created the standards to reduce exposure to hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) because the chemicals were proven to cause serious health effects.
Within this standard are HAPs that apply directly to the metal fabrication industries—known as Metal Finishing Hazardous Air Pollutants (MFHAPs). These are identified as materials that contain 0.1% by weight cadmium, chromium, lead, or nickel; or 1.0% by weight manganese. In order to regulate facilities that exhaust contaminated air straight outdoors, NESHAP Rule 6X went into effect on July 25, 2011.
Since the standards were introduced, many operations have installed dedicated dust and fume collection systems to safely collect MFHAPs. However, others still rely on standard HVAC systems or simply open the shop doors to release fumes directly to the atmosphere. Despite the importance of the rule and the length of time the EPA has been enforcing it, many facilities still may be unaware that they are not in compliance. Are you one of these facilities?
Here are a few key takeaways to help you better understand NESHAP Rule 6X:
Who is Impacted by NESHAP Rule 6X?
To find out if your facility is using MFHAP materials, consult the safety data sheets (SDSs) related to the materials you use (welding rod, welding wire, etc.). A standard SDS will list hazardous ingredients in Section 2. For example, if the material is shown to contain <2.50 % manganese by weight, the material is subject to the NESHAP 6X rule.
The rule applies to companies that are primarily engaged (50% or more total labor) in one or more of the following categories:
- Electrical and electronic equipment finishing
- Fabricated metal products
- Fabricated plate work (boiler shops)
- Fabricated structural metal manufacturing
- Heating equipment (except electric)
- Industrial machinery and equipment finishing
- Iron and steel forging
- Primary metal products manufacturing
- Valve and pipe fittings
Primary operations affected by the rule include:
- Welding
- Dry abrasive blasting (three types)
- Dry grinding
- Dry polishing with machines
- Dry machining
- Spray painting (two types)
This rule is highly applicable to welding shops; everyone engaged in welding needs to be aware of the rule and the required actions. Welding shops that rely on HVAC filtration to clean the air, exhausting welding fumes out to the atmosphere, are particularly at risk of being in violation of this EPA requirement. Even a dedicated dust and fume collection system may be in violation if it exhausts air outside and is older and/or not properly designed to handle the current processes.
Method 22 Fugitive Emissions Test
To determine if you are compliant with NESHAP Rule 6X, you must perform a Method 22 Fugitive Emissions Test. This test provides a visual determination of fugitive emissions from material sources. It's performed by an observer using two stopwatches.
The observer stands at least 15 feet from an exhaust stack—with a clear view of the exhaust and the sun at their back—and lines up a dark background. They run the first stopwatch continuously for 15 minutes. They start the second stopwatch when they start seeing emissions (opacity) and stops it when they can no longer see emissions. If opacity is observed during 20% or more of the 15-minute test period (3 minutes), Rule 6X applies.
Taking Action
If a facility fails a Method 22 test and Rule 6X applies, the facility must complete the following steps to achieve compliance:
- “Tier 1” response: Notify the EPA immediately. Change the process to eliminate the HAP. Changes may involve experimenting with different materials or settings to reduce emissions. It is important to remember that no matter what changes are made, equipment must always be operated in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Conduct another Method 22 test.
- “Tier 2” response: If the second test fails, “Corrective actions must take place immediately after the failed Method 22 test” per the Federal Register, page 42985, Welding compliance, Tier 2.
Using Cartridge Dust and Fume Collection to Comply with NESHAP Rule 6X
Installing dust and fume collectors with a high-efficiency cartridge filtration system like Camfil’s Gold Series X-Flo can offer multiple benefits in addition to maintaining EPA compliance. Cartridge filtration is identified within Rule 6X as an acceptable control device to eliminate visible emissions and it is the solution of choice in many cases.
A well-designed cartridge system will filter welding fumes and other hazardous contaminants effectively. The filtered air can either be recirculated back into the facility or exhausted outside. These systems use self-cleaning mechanisms that pulse dust and dirt off the filters, allowing units to run for extended periods between filter change-outs.
If a facility chooses to exhaust filtered air outdoors, NESHAP Rule 6X procedures will still apply. Contact the EPA Regional Office to find out which agency enforces the rule for your location. Under Method 22, the EPA requires ongoing annual compliance that is specific to the operation and is based on the date that the facility originally declares compliance.
Alternatively, if a facility opts to recirculate the filtered air instead of exhausting it outdoors, NESHAP Rule 6X no longer applies. But, the indoor air must still comply with OSHA permissible exposure limits (PELs). The collector may also require safety monitoring filters for added filtration and backup collection.
Air recirculation is the single best way to maximize your dust collector ROI. By recirculating heated or cooled air back through the plant instead of venting it outdoors, you eliminate the cost to replace that conditioned air. Many facilities report five- to six-figure annual energy savings as well as additional savings from earned utility rebates and incentives.
To learn more, download our full white paper, Is Your Welding or Abrasive Blasting Shop in Compliance with EPA’s NESHAP Rule 6X?
 Americas
Americas